Wake On Lan For Mac Os X
It is very small in size and requires very small connectivity to just hit the server. Flip it for mac. √ Online & Offline UseIt comes with offline progress saving mode. In common, Flip Range is fully free of the hassle. It is developed after long R&D for better functionality.
Introduction
Wake on LAN is a feature built into the NIC (the Ethernet card), and then the OS must support it too. This is one of the things, in the PC world, that determines one the differences between a. The intend of miniWOL is to have a small icon in your SysTray (Windows) or Menubar (MacOS X), where you can send a Wake On LAN magic packet to a defined server. All this without thinking or seeing all the in-depth details (once you’ve configured it right). To show miniWOL in action: miniWOL – Windows (left) and MacOS X (right). We’ve covered quite a few post related to Wake-On-Lan. In today’s post, we are going to cover how to wake up a Windows machine from a Mac and vice versa, waking up a Mac machine from Windows. If WOL concept is new to you, you should check out what it means to wake up a computer from a local network. How To Wake Up Windows Machine From Mac.
You answered many questions that Apple store workers could not. It truly is a workhorse and still running like a brand new computer.  Dear Jigs, your article is really helpful and informative – thank you so much for taking the time to post. I made the change to a Mac Pro desktop mid 2009 (and iPhones and iPads) and have never looked back!
Dear Jigs, your article is really helpful and informative – thank you so much for taking the time to post. I made the change to a Mac Pro desktop mid 2009 (and iPhones and iPads) and have never looked back!

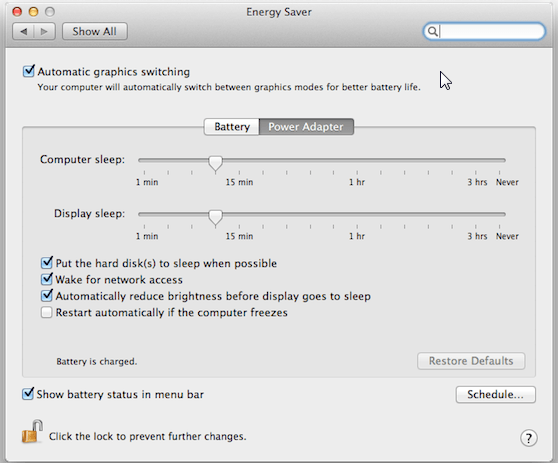
Wake on LAN (or WOL) allows you to remotely turn on a computer.
Note: WOL is available only on OS X 10.11 (El Capitan) or later.
Wake On Lan Mac Os X Command Line

Wake On Lan For Mac Os X 10.10
Enabling WOL on OS X
To enable WOL, do the following:
- For OSX it can be enabled from System Preferences ->Energy Saver by turning on Wake for network access.
- Restart the computer and boot into Recovery mode by holding CMD+R on boot until the Apple logo appears.
- Open Terminal from the Utilities menu.
- Disable System Integrity Protection by running the csrutil disable; reboot command.
- After OSX boots up, make sure you're logging in as an administrator and open Terminal from /Applications/Utilities/Terminal.app
- Log in as root by running the sudo -i command in the terminal window.
- Edit the boot configuration file by running the vim /Library/Preferences/SystemConfiguration/com.apple.Boot.plist command.
- Press i to enter Insert mode. Find the Kernel Flags and change it to Kernel Flags darkwake=0
- Press Esc, then input :wq and press Enter to save the file and quit vim.
- Run the reboot command.
- Boot into Recovery mode by holding CMD+R on boot time.
- Open Terminal from Utilities menu.
- Re-enable System Integrity Protection by running the csrutil enable; reboot command.
- After OSX boots up, disable the Password Requirement after sleep, by opening System Preferences >Security & Privacy, selecting the General tab, and unchecking the Require password field.
